
Diabetes and heart disease often go hand in hand, forming a dangerous partnership that can significantly impact an individual’s overall health and well-being. Diabetes, specifically type 2 diabetes, has been closely associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular conditions. Understanding the connection between diabetes and cardiac health is crucial for effective prevention, management, and improved outcomes for individuals living with this chronic condition.

Diabetes has been identified as a major risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease (CVD). High blood sugar levels, a hallmark of diabetes, can damage blood vessels and promote the buildup of fatty deposits, leading to atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of arteries) and an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
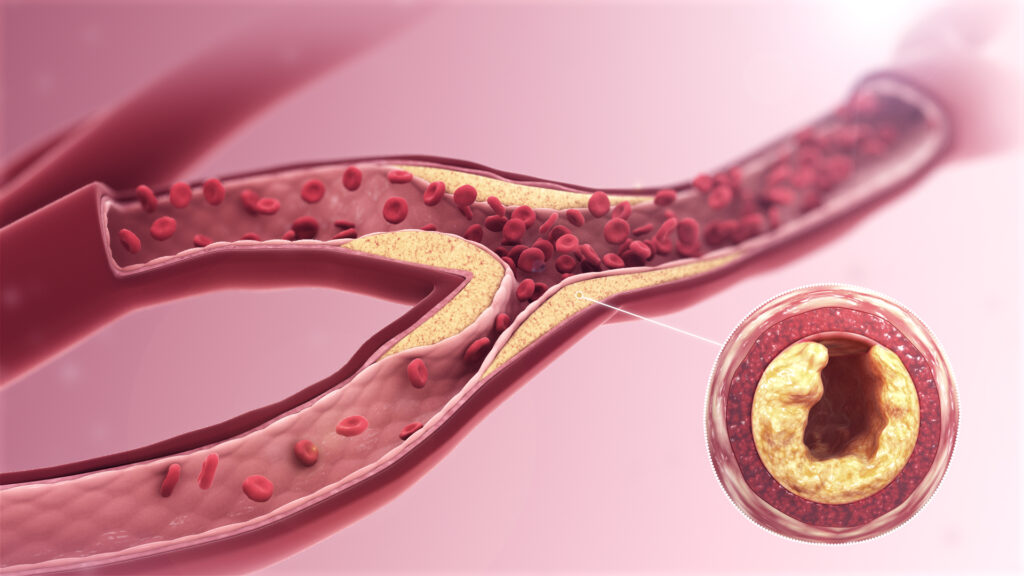
Diabetes can also impact the structure and function of the heart itself. It can lead to diabetic cardiomyopathy, a condition characterised by changes in the structure and function of the heart muscle, reducing its ability to pump blood efficiently. This can result in heart failure and other cardiac complications.
Individuals with diabetes often experience other risk factors contributing to poor cardiac health, such as hypertension (high blood pressure) and dyslipidaemia (abnormal cholesterol levels). These factors further increase the risk of heart disease and related complications.
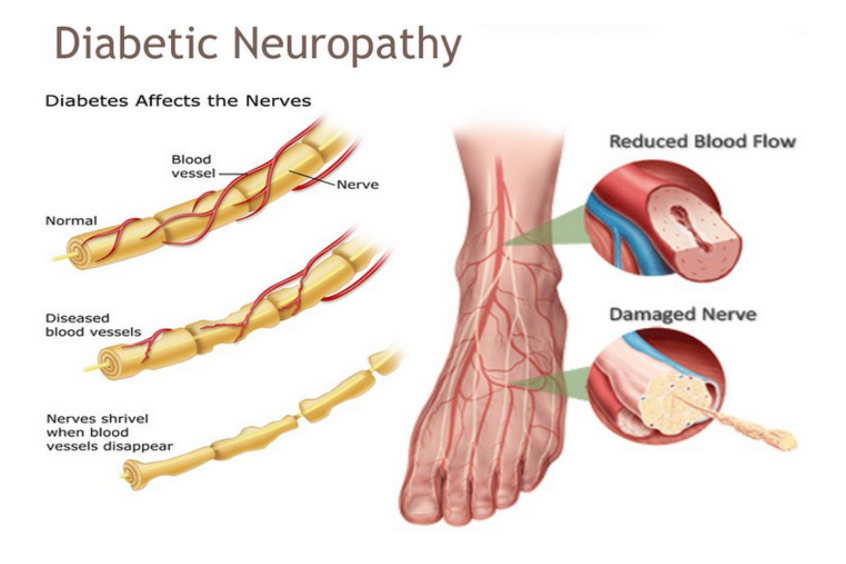
Diabetes can damage the nerves that control the heart and blood vessels, a condition known as diabetic autonomic neuropathy. This can disrupt normal heart rhythm (arrhythmias) and impair the ability of blood vessels to dilate and constrict, leading to blood pressure instability.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is paramount in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetes-related cardiac complications. Regular monitoring, adherence to prescribed medications, a healthy diet, and regular physical activity are crucial components of glycaemic control.
Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels is vital for reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. This may involve lifestyle modifications, such as a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, and medication as prescribed by healthcare professionals.
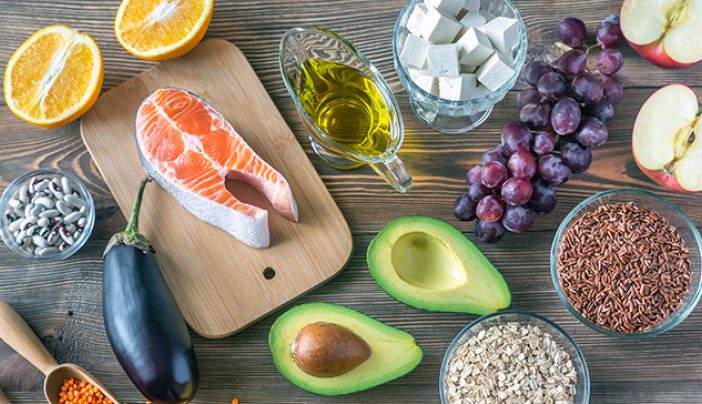

Adopting a healthy lifestyle is beneficial for both diabetes management and cardiac health. It includes regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, smoking cessation, limited alcohol consumption, and stress management.
Individuals with diabetes should receive regular medical check-ups and monitoring of cardiac health parameters, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and heart function. Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential to tailor a personalized care plan and address any emerging concerns promptly.

The relationship between diabetes and cardiac health is profound, with diabetes acting as a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease and cardiac complications. Understanding the connection empowers individuals with diabetes to take proactive steps in preventing and managing these risks effectively. Through vigilant glycaemic control, blood pressure and cholesterol management, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular medical care, it is possible to mitigate the impact of diabetes on cardiac health and improve overall well-being. By prioritizing heart health, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while reducing the burden of cardiovascular disease.


Be the first to comment